SWIFT’s Customer Security Programme (CSP) helps financial institutions ensure their defences against cyberattacks are up to date and effective, to protect the integrity of the wider financial network. Users compare the security measures they have implemented with those detailed in the Customer Security Controls Framework (CSCF), before attesting their level of compliance annually.
With solid attestation and compliance rates, the CSP reflects a community of highly engaged users committed to stopping cyberattacks in their tracks. And, as the cyber threat landscape evolves, so too does the CSP.

- Why is this important?
- How will this impact SWIFT customers?
- Key milestones your organisation needs to know
- Conditions for successful implementation of the SWIFT CSP
Why is this important?
At the end of 2015, a bank in Vietnam was hacked and became the victim of a cyber attack on the SWIFT system, when attackers aimed to steal USD 1.36 million from the bank's account. In 2016, an increase in the number of cyberattacks on the SWIFT system was reported globally with the most severe case being a compromise by the Central Bank of Bangladesh resulting in fraudulent remittance instructions with total value of $951 million, of which $101 million was handled by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
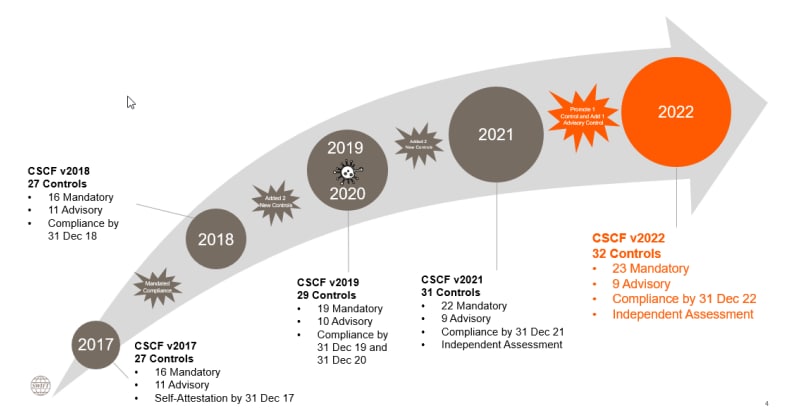
In response to cyberattacks and breaches throughout 2015-2016, in 2017 SWIFT issued 16 mandatory and 11 optional security controls to all 11,000 customers worldwide. All clients are required to attest to meeting annual controls and the results of this are shared with partners and regulators.
How will this impact SWIFT customers?
SWIFT CSP has evolved and will continue to do so since its inception. Customers will need to continue to implement security controls and elevate limits to ensure CSCF compliance. Previously, SWIFT customers were required to self-certify CSCF v2019 by December 31, 2019. This updated framework includes 19 required security controls and 10 advisory security controls.
In 2020, SWIFT made 2 existing advisory controls mandatory and introduced 2 new advisory controls resulting in 21 mandatory and 10 advisory controls in CSCF v2020.
By 2021, SWIFT converts 01 advisory control into mandatory, thereby increasing the number of mandatory controls to 22 controls and 9 advisory controls in CSCF v2021. As of mid-2021, organizations will need to support their attestation of CSCF v2021 with an internal audit or an independent audit conducted by a third party.
In July 2021, SWIFT published the CSCF v2022 with 23 mandatory and 9 advisory controls respectively, against which organisations will need to attest in the second half of 2022.
The CSCF Working Group centralised, prioritised and reviewed all feedback from the community prior to finalising the changes shown in the picture below
Key milestones your organisation needs to know
Source: https://www.swift.com/
Conditions for successful implementation of the SWIFT CSP
To comply with SWIFT CSP requirements, organizations need to adopt a systematic approach that requires coordination across the three lines of defence, leadership support, and a team of stakeholders. Diverse members have full knowledge of professional profession. Is your organization ready to respond to the compliance requirements from SWIFT CSP?
Why PwC?
Proven experience in assessing and auditing SWIFT CSP
- We have conducted many SWIFT CSP audits and assessments across many territories and industries including CEE.
SWIFT Knowledgeable Advisory Team
- We are knowledgeable about the security requirements of SWIFT and our team consists of qualified domestic and foreign IT security experts with experience in assessing and reviewing SWIFT systems. Our professionals are part of the global SWIFT CSP network.
Adapt to the requirements of the organization
- PwC will leverage in-house developed libraries/guidelines combined with extensive SWIFT CSP expertise and knowledge to provide tailored recommendations that support the organization's controls to timely comply with SWIFT’s requirements.
SWIFT CSP: Frequently Asked Questions
- What is SWIFT CSP?
- When is the deadline for SWIFT CSP compliance?
- What form should the independent assessment of SWIFT perform?
- What are the 23 mandatory controls of SWIFT CSP?
- What happens if the organization does not comply?
- What if I suspect the organization is being targeted by cybercriminals or is violating SWIFT's control requirements?
What is SWIFT CSP?
SWIFT Customer Security Program (CSP) aims to prevent and detect fraudulent activity through a series of mandatory security controls, community-wide information sharing activities, and advanced security features on their products.
When is the deadline for SWIFT CSP compliance?
SWIFT customers are required to submit their attestation annually to SWIFT's KYC portal by December 31 of each year.
In 2020, customers can attest to compliance with CSCF v2019 or CSCF v2020. From 2021, an independent review with customer attestation is required.
What form should the independent assessment of SWIFT perform?
There are two ways in which SWIFT customers can obtain an independent review:
- Internal audit: This is similar to an internal audit, which is performed by the client's internal audit team/department or a tailored independent team that operates and submits attestation.
- Independent external assessment: This is similar to an external audit, conducted by organizations such as PwC, who will provide an independent review of the SWIFT CSP's controls.
What are the 23 mandatory controls of SWIFT CSP?
There are 23 mandatory controls that focus on protecting the organization's environment, identifying and restricting access, detection, and response.
What happens if the organization does not comply?
SWIFT reports all cases of non-compliance and instances of unattested members to domestic regulatory authorities. In addition, SWIFT will select an attestation form to verify each year.
What if I suspect the organization is being targeted by cybercriminals or is violating SWIFT's control requirements?
It is important for an organization to share all relevant information with SWIFT about an organization experiencing an incident as soon as possible, in order to obtain timely assistance and also to protect other organizations in the network.